(My latest for Catholic Answers Magazine.)
When were the Gospels written?
You might respond with a question of your own: “Who cares?” Or, “Why does it matter?”
Here’s one reason why: some skeptics are claiming that the Gospels are unreliable accounts of Jesus’ life because they were written too long after the fact. They then use the alleged unreliability of the Gospels as a weapon against Christianity.
For example, the quite popular (and quite skeptical) New Testament scholar Bart Ehrman states in his book How Jesus Became God that the Gospel authors had no intent of presenting “biographical information” concerning “what Jesus really said and did.” Skeptics like Ehrman maintain that accounts of Jesus’ career were passed down orally for many decades before they were ever written down in the Gospels, leaving them open to be embellished until they bore little to no resemblance to what actually took place during Jesus public ministry during A.D. 30-33. To their reckoning, the process of Gospel composition was like the children’s game of Telephone, in which a message, whispered from one ear to another, gets changed many times before it reaches its final destination. This despite the evangelists’ claims to be reporting the truth about Jesus’ career (cf. Luke 1:1-4; John 19:35, 21:24-25).
Ehrman contends, along with the majority of modern textbooks on the New Testament, that the Gospels were composed decades after the life of Christ, with Mark circa A.D. 69-70, Matthew and Luke in the 70s or possibly the 80s, and John in the 90s, possibly as late as 95. Ehrman is sure that the forty- to sixty-year gap between Jesus’ life and the appearance of his biographies lessens the probability that they preserve accurate information about him.
But there is another view, long dormant, that is reasserting itself on the scene: the idea that, just maybe, the Gospels were written much earlier. Years ago, the scholar John A.T. Robinson claimed that the entirety of the New Testament was composed prior to A.D. 70! Why? For the simple reason that not one of the twenty-seven New Testament books mentions the destruction of the Jerusalem Temple by the Romans in that year—a cataclysmic event of cosmic significance for Jews.
Now, I can hear what some of you are saying: “But Jesus prophesied the destruction of the temple!” True, but it wasn’t prophecy ex eventu (“after the fact”), with the Gospel writers reading some recent event back into Jesus’ words years before. (If that was the case, the evangelists did a terrible job.) No, this was real prophecy, for Jesus spoke of the temple stones being “thrown down,” whereas the temple was actually burned to the ground. If the Gospel writers were aware of how the temple actually was destroyed, they might have mentioned that, because fire is a well-known biblical image of judgment.
It defies belief that no New Testament book, if written after the year 70, would have mentioned the temple’s decimation in clear fashion, especially given the role of the temple authorities in Jesus’ death. (Hebrews 13:10 implies that the temple is still standing at the time of its writing: “We have an altar from which those who minister at the tabernacle have no right to eat.”) If the temple really had been lying in ruins when the New Testament writers put ink to scroll, the temptation to say, “Hey, here’s God’s judgment on the temple authorities for what they did to Jesus!” would have been too great to ignore.
And there are other reasons the Gospels might have been written earlier. The Acts of the Apostles leaves off with Paul in Rome under house arrest, awaiting trial. It’s highly doubtful that Luke, the author of Acts and traveling companion of Paul, would not discuss the martyrdom of the book’s central figure—not to mention that of Peter, who was also martyred circa A.D. 64 under the Neronian persecution. So there’s a good case to be made that Acts was composed pre-70; in fact, pre-64!
We also know that Acts is part two of Luke’s “two-volume set,” as it were, with the Gospel of Luke being part one, so obviously Luke’s Gospel had to come even earlier. And, if Mark was indeed written prior to Luke, serving as a source for that Gospel and for Matthew (as most scholars believe), Mark must date earlier still.
And don’t forget that Paul’s letters, which corroborate many facts about Jesus’ life, were probably written prior to any of the Gospels.
Now, if the Gospels really were written later, as Ehrman and many scholars assert, it doesn’t necessarily follow that they are historically unreliable. But we’d probably all agree that the closer in time a document is written to the events it covers, the more likely it is that it’s accurate and, just as importantly, can be verified by others.
An experience I had might help us to understand this. While visiting the Catholic Answers offices in San Diego not long ago, my family and I took a side trip to see Torrey Pines, the gorgeous golf course that hugs the Pacific coast. Not far from the course we stumbled upon a beautiful veterans’ monument, honoring those who had given their lives in service to their country. Many of those memorialized had served in the Vietnam War, which ended in 1975. Of course, many veterans of that conflict are still alive today, with still-vivid memories of their tours of duty.
This all reminded me of an insight from the Evangelical writer Greg Monette: the period of time that has elapsed since the Vietnam War until the present day is pretty much exactly the same time frame that elapsed—if the earlier dates are right—between the public ministry of Jesus and the time when the Gospels were likely completed and circulating: about forty years. Just as someone today offering an erroneous, fictional account of the Vietnam conflict could be discredited by the testimony of those who were actually there and lived through the experience, the controlling influence of eyewitnesses to Jesus’ ministry would have prevented the Gospel writers from fabricating events from Jesus’ career that never really happened.
Even if the Gospels had been written later, on Ehrman’s timeline, that would be about the same gap from World War II to the present day. Just as there aren’t as many World War II vets still living as Vietnam vets, there are still some who could be interviewed. Paul noted in 1 Corinthians 15:6 that many of the over 500 individuals who witnessed the resurrected Christ on one occasion were alive, and ostensibly willing to be consulted. New Testament scholar Robert McIver contends that there would have been up to 63,000 potential adult witnesses to Jesus’ public career, with 18,000 to 20,000 still living after thirty years (which would correspond to the earlier dates of Gospels composition) and between 600 and 1,100 within sixty years (the later dates). An early apologist named Quadratus, who lived from 70-130 AD, also claims that eyewitnesses to Jesus were alive in his day.
As the Acts of the Apostles notes, “This was not done in a corner” (Acts 26:26), or in a galaxy far, far away. Whatever the exact dating of the Gospels, Jesus’s ministry was a public event whose chroniclers were intent on accuracy and whose witnesses were not going to stand by to let what they had seen and heard be swallowed up in legend.
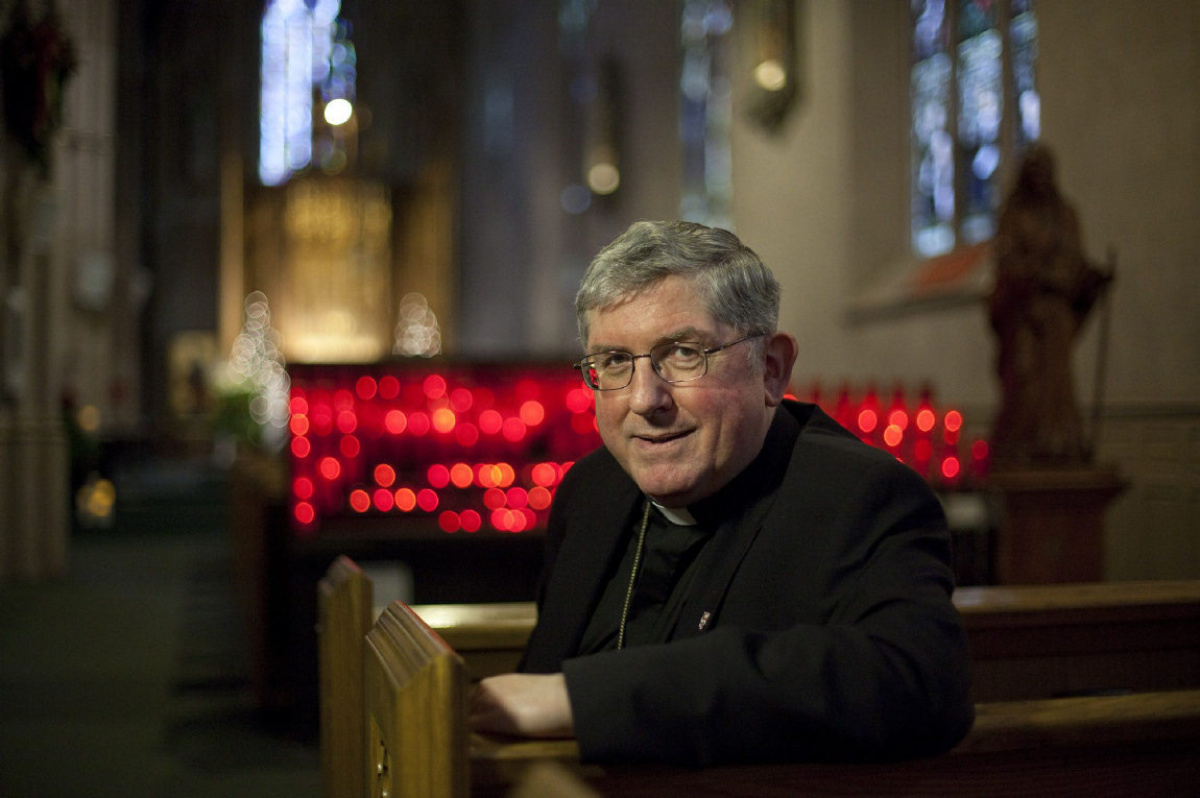






 Cardinal Thomas Collins, Archbishop of Toronto, penned a powerful letter today to Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau regarding the Trudeau government’s regrettable recent decision to donate $650 million to international organizations that promote abortion and contraception.
Cardinal Thomas Collins, Archbishop of Toronto, penned a powerful letter today to Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau regarding the Trudeau government’s regrettable recent decision to donate $650 million to international organizations that promote abortion and contraception.

